Understanding Inflammation and Its Effects on the Body
Inflammation is a fundamental physiological response triggered by the body in reaction to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli. This process is primarily a defence mechanism aimed at healing damaged tissues and warding off pathogens. Inflammation can be classified into two categories: acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation is a short-term response that typically presents with noticeable symptoms such as redness, heat, swelling, and pain. This process is essential for recovery, allowing the body to repair itself effectively.

Conversely, chronic inflammation is a prolonged and often low-grade form of inflammation that persists for an extended period. It can occur without any apparent symptoms, making it particularly insidious. This condition has been associated with various diseases, including arthritis, heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. The continued activation of the inflammatory response in the absence of acute injury or infection can lead to significant damage to healthy cells, tissues, and organs.
Poor dietary choices

Poor dietary choices can exacerbate chronic inflammation. Diets high in processed foods, refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives can trigger inflammation. For instance, trans fats found in some fried and packaged foods can promote inflammatory responses in the body. Additionally, excessive consumption of sugar and refined carbohydrates has been linked to elevated levels of inflammatory markers in the bloodstream. These dietary habits can hinder the body’s natural ability to maintain a balanced inflammatory response, contributing to the development and progression of chronic diseases.
Recognizing the body’s inflammatory responses is crucial for understanding how to mitigate their effects through dietary strategies. By making informed food choices and emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods, individuals can potentially reduce the risk of chronic inflammation and improve their overall health. Following this foundational knowledge, the subsequent sections will delve into practical dietary guidelines aimed at promoting a healthier lifestyle through the reduction of inflammation.
Key Dietary Components That Combat Inflammation
One of the essential ways to mitigate inflammation is through a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods. This dietary approach emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and specific spices known for their beneficial properties. Each of these food categories contributes uniquely to the body’s ability to fight inflammation.
Fruits and vegetables
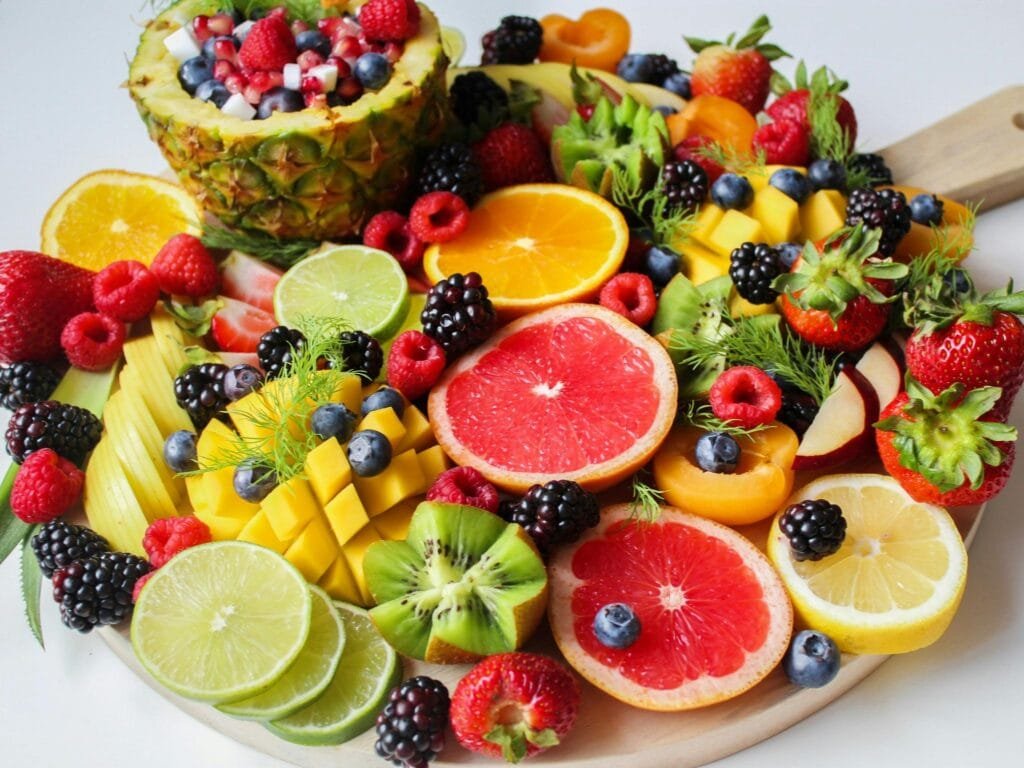

Fruits and vegetables are at the forefront of this anti-inflammatory diet. They are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which neutralize free radicals in the body. For instance, berries such as blueberries and strawberries are particularly high in flavonoids, which have been shown to reduce inflammatory markers. Leafy greens, such as kale and spinach, contain various phytonutrients that further contribute to this anti-inflammatory effect by supporting the immune system.
Whole Grains

Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, provide essential nutrients along with fiber, which aids digestive health. This fiber-rich component is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a significant role in regulating inflammation. Whole grains also help manage blood sugar levels, preventing spikes that can trigger inflammatory responses.
Lean proteins

Lean proteins, such as fish and poultry, offer vital amino acids and omega-3 fatty acids in particular—found abundantly in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel—are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties. Omega-3s are known to inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines and promote overall heart health.
Healthy fats, particularly from sources like avocados, olive oil, grass-fed beef, and nuts, also play a significant role. These fats are rich in monounsaturated fats, which have been associated with reduced markers of inflammation. Furthermore, spices such as turmeric and ginger are noteworthy for their active compounds—curcumin and gingerol, respectively—that have been extensively studied for their potent anti-inflammatory effects.
Finally, it is crucial to avoid processed foods and refined sugars as they can promote inflammation in the body. These foods often contain high levels of trans fats and added sugars, contributing to weight gain and metabolic disturbances, further exacerbating inflammatory conditions.
Creating an Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan

Implementing an anti-inflammatory meal plan can be both straightforward and enjoyable. To begin with, prioritizing whole foods rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and fibre is essential. A well-balanced anti-inflammatory diet typically includes an array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. For effective meal prepping, consider starting each week by determining your main meals and snacks to ensure a consistent intake of anti-inflammatory nutrients.
One approach could be to prepare a weekly menu featuring a variety of flavours and textures. For breakfasts, consider recipes like overnight oats topped with berries and chia seeds. This meal not only provides fiber but is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids. For lunch, a quinoa salad adorned with mixed greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, avocados, and a lemon-tahini dressing can be both refreshing and nourishing. The inclusion of avocados introduces healthy fats, which are integral in combating inflammation.
Dinners can feature grilled salmon, known for its omega-3 content, paired with a side of steamed broccoli and sweet potatoes. Incorporating spices like turmeric or ginger into your meals can enhance their anti-inflammatory effects. Meal prep can be further simplified by cooking larger portions, allowing for leftovers that can be easily reheated throughout the week.
Grocery shopping is a crucial part of successfully following an anti-inflammatory diet. Aim to fill your cart with a diverse selection of fresh produce, whole grains such as brown rice or quinoa, legumes, nuts, and seeds. When shopping, make a habit of reading labels to avoid processed foods high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats. By integrating healthy substitutions into your favorite recipes, you can create delicious meals while effectively reducing inflammation.
Additional Lifestyle Changes to Support Inflammation Management

While diet plays a pivotal role in managing inflammation, it is essential to recognize that other lifestyle factors contribute significantly to overall health and inflammation reduction. One key aspect to consider is physical activity. Engaging in regular exercise can help modulate the body’s inflammatory response. Not only does physical exercise improve circulation and reduce stress levels, but it also promotes the release of endorphins, which can enhance mood and overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, complemented by strength training exercises on two or more days, to support your inflammation management efforts.
In addition to exercise, effective stress management techniques can significantly influence inflammation levels. Chronic stress is known to trigger inflammatory responses in the body, making practices like mindfulness and yoga incredibly beneficial. Mindfulness meditation encourages individuals to focus on the present moment, thus reducing stress and anxiety. Furthermore, yoga combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation, which can help lower levels of cortisol—a hormone associated with stress—that, when elevated, can fuel inflammation. Dedicating time to these practices can lead to profound improvements in both emotional and physical health.
Lastly, adequate sleep is a critical component in the fight against inflammation. Poor sleep quality and sleep deprivation can exacerbate inflammation and increase susceptibility to various health conditions. Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night to support your body’s recovery processes and immune function. Establishing a bedtime routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and limiting screen time before bed can promote better sleep hygiene.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes alongside a healthy diet will foster a holistic approach to reducing inflammation and enhancing overall health and wellness.