Understanding the Glute Muscles
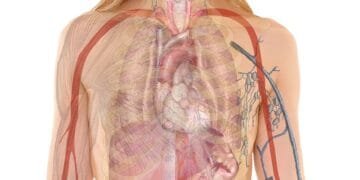
The gluteal muscles, often referred to as the glutes, are a group of three key muscles located in the posterior region of the body: the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. Each of these muscles plays a vital role in various bodily movements and overall stability. Understanding their anatomy and functions is crucial for anyone looking to strengthen this muscle group, enhance athletic performance, and prevent injuries.
The gluteus maximus is the largest and most powerful of the three muscles, responsible for hip extension, outward rotation, and the stabilization of the pelvis. This muscle is heavily engaged during activities such as running, climbing, and standing from a seated position. Strengthening the gluteus maximus not only enhances performance but also aids in maintaining proper alignment of the spine and hips, promoting good posture.
The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus, while smaller, are equally important. The gluteus medius is located on the side of the hip and is primarily responsible for hip abduction and stabilization of the pelvis during single-leg activities. This muscle plays a critical role in movements such as walking and running, where maintaining balance and proper gait mechanics is essential. The gluteus minimus, although the smallest of the trio, assists in similar functions, contributing to hip abduction and internal rotation.
Strong glute muscles are not only essential for athletic activities but also for everyday movements. They play a significant role in injury prevention by supporting the knees and lower back. Weak glutes can lead to compensatory patterns in other muscles, increasing the risk of strain or injury. Therefore, prioritizing glute strength can significantly enhance an individual’s overall physical performance and quality of life.
Essential Exercises for Glute Strengthening
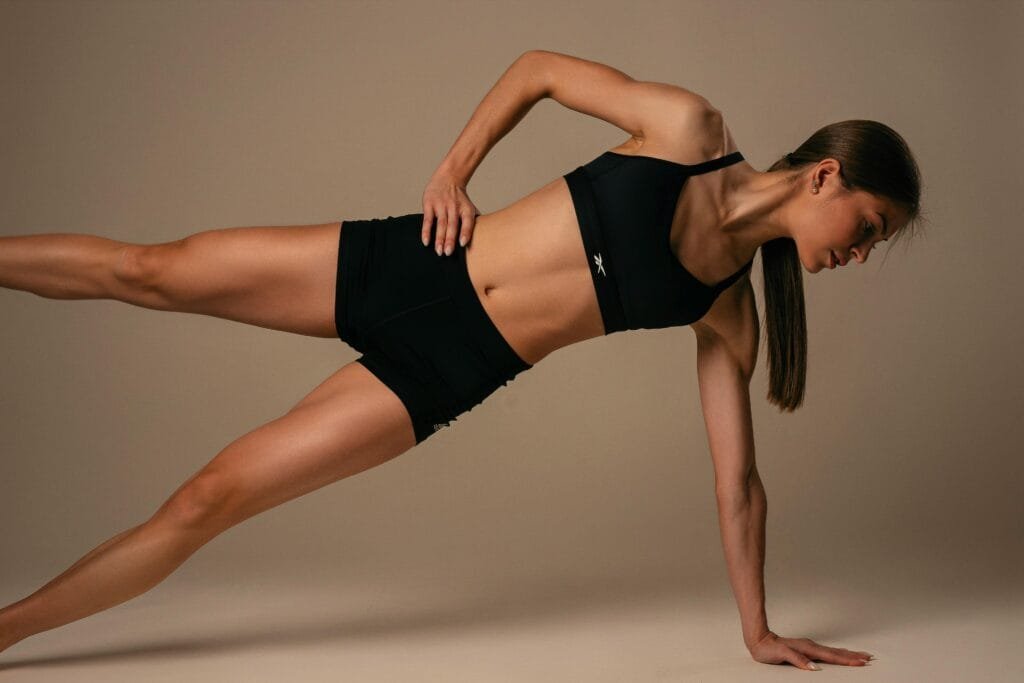

Building stronger, toned glutes is a crucial aspect of any fitness regimen, emphasizing both aesthetics and functional strength. Incorporating a range of exercises, including compound and isolation movements, will yield optimal results. Below, we explore several key exercises, their proper execution, common errors to avoid, and variations suitable for different fitness levels.
Squats are foundational to glute development, promoting functional strength. Begin with feet shoulder-width apart, keeping your chest up and back straight. Lower your body by bending your knees, ensuring they remain aligned with your toes until your thighs are parallel to the floor. Avoid letting your knees cave in or your back round during descent. To enhance the difficulty, try variations such as goblet squats or sumo squats.
Lunges are another effective exercise that targets the glutes while improving balance. Start with a standing position and step forward with one leg, lowering your hips until both knees form 90-degree angles. Ensure the front knee does not extend beyond your toes and maintain an upright posture. To increase the challenge, incorporate reverse lunges or walking lunges into your routine.
Hip thrusts directly focus on the glutes, making them a vital addition. Position your upper back against a bench, with feet flat on the floor and knees bent. Push through your heels to lift your hips until your knees, hips, and shoulders form a straight line. Avoid overarching your back at the top. For added difficulty, place a weighted plate on your hips or perform single-leg variations.
Deadlifts are a compound movement that engages multiple muscle groups, including the glutes. Stand with feet hip-width apart and grip a barbell or dumbbell at your shins. Keeping your back neutral, hinge at the hips and lower the weights while maintaining the spinal position. Common mistakes include rounding the back or letting the weights drift away from the body. Variations such as sumo deadlifts or Romanian deadlifts can further enhance glute activation.
Incorporating a balanced mix of these exercises into your workout routine will significantly contribute to developing stronger, toned glutes while ensuring comprehensive muscular engagement.
Creating a Workout Plan for Glute Development
When building a workout plan for glute development, it is essential to establish a structured approach that incorporates specific exercises targeting the glute muscles, while also considering overall fitness goals. A well-rounded glute workout typically consists of compound movements, isolation exercises, and progressive overload to enhance muscle strength and tone. Key exercises include squats, deadlifts, and lunges, which activate multiple muscle groups and are effective for stimulating gluteal growth.
To ensure optimal results, pay attention to both volume and intensity. Volume refers to the total amount of work performed, measured by sets and repetitions. For glute-focused workouts, aim for three to five sets of eight to twelve repetitions per exercise. This range is generally considered ideal for muscle hypertrophy, targeting growth in the glute muscles. Intensity is equally important; it involves the weights used and how challenging the exercises are. Gradually increasing the weight or adjusting resistance levels can help maintain progressive overload, essential for continued strength gains.
Frequency is another important aspect when creating a glute workout plan. Training glutes two to three times per week is recommended for most individuals. This frequency allows for adequate recovery while still promoting muscle growth. For those new to glute training, start with two sessions per week, gradually increasing to three as your body adapts. Integrating glute-focused exercises into a full-body routine can also be beneficial. For example, incorporating glute bridges or hip thrusts into upper-body workout days ensures that glute work is balanced throughout the week.
As you develop your plan, consider incorporating sample workouts based on your experience level. Beginners may focus on foundational movements with lower weight, while advanced athletes can incorporate heavier lifts and more complex variations. By thoughtfully structuring your workout plan, you can unlock the potential for stronger, toned glutes effectively.
Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Results

Achieving stronger, toned glutes requires a rigorous training regimen and a well-balanced approach to nutrition and recovery. Nutrition plays a vital role in muscle repair and growth, particularly in the gluteal muscles. A key component of this nutritional strategy is adequate protein intake. Protein serves as the building block for muscle tissue and consuming sufficient protein aids in the recovery process after workouts. High-quality protein sources include lean meats, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based protein options. Aim for a protein intake that supports your training intensity and overall fitness objectives, ideally consuming protein shortly after exercising to maximize muscle repair.
Hydration is another essential element in optimizing glute performance. Staying well-hydrated allows for better circulation, which in turn facilitates the delivery of nutrients to muscle tissues. Dehydration can impair physical performance and hinder recovery, ultimately affecting your progress in achieving toned glutes. Therefore, ensure that you are drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after workouts.
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet is equally important. Fats play a crucial role in hormone production, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. Include sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in your meals to support your overall nutrition strategy.
Aside from nutrition, effective recovery strategies are critical for optimal glute performance. Allocating specific rest days allows your muscles to recover and rebuild, preventing injury and fatigue. Stretching and foam rolling can enhance flexibility and reduce muscle soreness, encouraging better glute engagement during your workouts. These recovery practices, when combined with a balanced nutritional plan, will enhance your training efforts and contribute significantly to achieving your goal of stronger, toned glutes.