Introduction to the Issue
The consumption of soda among children has become a significant public health concern, particularly due to its detrimental effects on dental health. Over recent years, there has been a troubling trend of increasing soda intake within this demographic. Reports indicate that many children have incorporated sugary beverages into their daily routines, often replacing healthier options such as water. This shift not only contributes to poor dietary habits but also raises questions about the long-term implications for children’s holistic well-being.
Soda is typically laden with high levels of sugar, contributing to calorie excess and increased risk of obesity. However, its implications extend far beyond weight gain; the sugar content directly affects dental health. When children consume sugary drinks, the mouth’s bacteria metabolize these sugars, producing acids that erode tooth enamel. This can lead to cavities, gum disease, and other oral health issues at an alarming rate. Recent studies underscore the troubling correlation between high soda consumption and a spike in dental problems among children, which are often rooted in inconsistent oral hygiene practices.
The potential for dental decay is compounded by the acidity found in many sodas, which not only weakens enamel but can also irritate the gums, further exacerbating oral health challenges. Children are particularly vulnerable due to their developing teeth and often inadequate dental hygiene awareness. As parents and guardians, understanding the connection between soda consumption and dental health is essential for fostering healthier habits.
In summary, the rising trend of soda intake among children is concerning not only for their physical health and mental health but notably for their dental health, presenting a multidimensional challenge that requires attention from parents, educators, and public health advocates alike.
Understanding Dental Health in Children
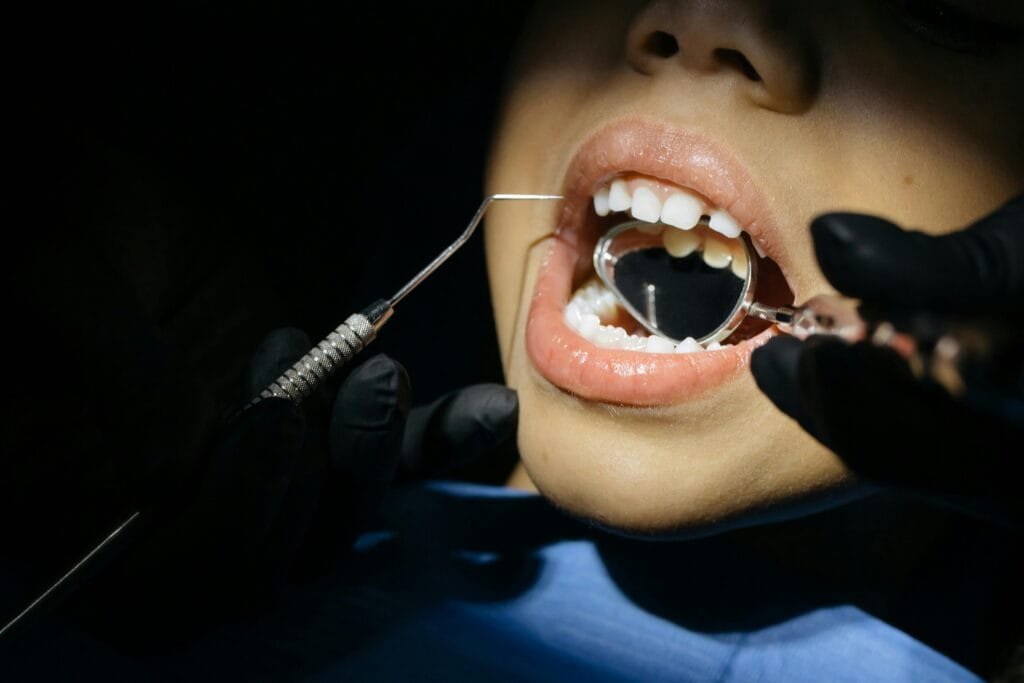
Dental health in children is a crucial aspect of their overall well-being. This includes not only the presence of strong and healthy teeth but also the absence of common dental problems such as cavities and enamel erosion. As children undergo significant growth and development, their oral health can directly impact their ability to eat, speak, and socialize effectively. Thus, understanding the factors that influence dental health is essential for parents and caregivers.
Cavities, also known as dental caries, are one of the most prevalent issues affecting children. They occur when bacteria in the mouth produce acid that erodes the tooth’s enamel, leading to painful decay. Factors contributing to cavities emphasize the importance of nutrition and oral hygiene. Consuming sugary snacks and drinks, including soda, apple juice, can significantly increase the risk of cavities. This is particularly concerning as many children have diets high in sugar and acids that contribute to enamel erosion.
Enamel erosion is another common dental issue among children. It occurs when the tooth’s protective layer wears away, making teeth more susceptible to decay and sensitivity. Factors such as poor oral hygiene practices, high consumption of acidic foods and beverages, and a lack of fluoride can exacerbate this condition. Establishing a solid foundation of good oral hygiene habits from an early age is essential in preventing enamel erosion and other dental health problems.
To foster healthy dental habits, parents should encourage regular brushing and flossing, limit sugary snack intake, and promote regular visits to the dentist. These practices not only help prevent cavities and enamel erosion but also instill lifelong habits that contribute to maintaining good dental health throughout their lives. Understanding and addressing these issues is vital for ensuring that children’s dental health remains robust as they transition into adulthood.
The Composition of Soda and Its Effects on Teeth
Soda is a popular beverage choice among children, often due to its sweet taste and appealing branding. However, the composition of soda raises significant concerns regarding dental health. The primary ingredients that pose risks to oral hygiene are sugars and acids. Most soft drinks contain high levels of added sugars, such as sucrose and high fructose corn syrup. These sugars serve as food for bacteria present in the mouth, leading to the production of acids that can erode dental enamel.
In addition to sugars, the acidic nature of many sodas exacerbates the potential for dental damage. Common acids found in soft drinks, including citric acid and phosphoric acid, contribute to a lower pH level in the mouth. When the pH drops, the environment becomes conducive for enamel demineralization, a process where minerals are leached from the teeth. This demineralization can lead to the formation of cavities, making it crucial to understand how soft drink consumption can impact long-term dental health.
The interaction between sugars and acids in soda creates a harmful cycle for children’s teeth. Upon consumption, soda can lead to an initial spike in bacteria’s activity due to the presence of sugars. As these bacteria metabolize the sugars, they produce additional acids, further contributing to enamel erosion. Over time, this can result in significant dental problems, including sensitive teeth, tooth decay, and increased risk of gum disease. Thus, the ingredients in soda not only pose immediate risks but can also lead to chronic dental issues if consumed frequently. Addressing the consumption of these beverages is essential for maintaining children’s dental health and preventing potential complications.
Recent Research Findings
Recent studies have significantly contributed to our understanding of the impact of soda consumption on children’s dental health. Research published in esteemed peer-reviewed journals indicates a clear correlation between the frequent intake of sugary beverages and the incidence of dental caries among young individuals. For instance, a longitudinal study conducted by the American Dental Association revealed that children who consume soda more than three times a week exhibit a 30% higher risk of developing cavities compared to those who do not include soda in their diets.
Additionally, a comprehensive report from the World Health Organization emphasizes the detrimental effects of acidic soda components on tooth enamel. The report outlines that the high acidity in soft drinks can erode enamel, which is critical for protecting teeth from decay. As a result, children who regularly consume sodas are prone to enamel erosion, leading to increased sensitivity and a higher likelihood of tooth decay over time.
Another significant finding from a study published in the Journal of Public Health Dentistry highlights the socioeconomic factors associated with soda consumption and dental health. It concludes that children from lower-income households are more likely to consume sugary drinks daily, leading to poorer dental outcomes. This highlights not only the need for increased awareness among parents and guardians regarding the importance of limiting soda consumption but also underscores the role of community health initiatives aimed at providing healthier beverage options.
Moreover, educational interventions targeting children have shown promise. Programs that educate youngsters about the adverse effects of soda on oral health have resulted in a noticeable decrease in soda consumption and a corresponding improvement in overall dental health. Thus, ongoing research continues to illuminate the various dimensions of soda’s impact on children’s dental well-being, reinforcing the importance of informed dietary choices in promoting healthy teeth.
Long-term Consequences of Soda Consumption
The consumption of soda, particularly among children, has been a growing concern in relation to dental health. Regular intake of sugary beverages can lead to a range of chronic dental problems that extend well into adulthood. The primary issue stems from the high sugar content in sodas, which contributes significantly to the formation of cavities. When sugars are metabolized by bacteria in the mouth, they produce acids that erode tooth enamel, paving the way for caries formation.
Beyond cavities, children who consume soda regularly may also experience a greater risk of enamel erosion. This condition occurs when the protective layer of the teeth is worn away, leading to increased sensitivity and susceptibility to further decay. Over time, the cumulative effects of soda consumption can result in serious dental issues, including gum disease and tooth loss. Such conditions not only affect aesthetic appearance but can also hinder proper chewing and biting functions.
The treatment for these dental problems can be extensive and costly. Dental procedures may include fillings, root canals, crowns, or even orthodontic interventions in severe cases. This can pose a financial burden on families and also contribute to stress for children, who may require frequent visits to the dentist. The implications of poor dental health are far-reaching, as studies have shown connections between oral health and overall health. Chronic dental issues can influence a child’s nutritional choices, potentially leading to obesity, as discomfort from dental pain may restrict their ability to consume certain foods.
In light of these factors, it becomes essential for parents and caregivers to be aware of the potential long-term consequences of soda consumption on children’s dental health. Establishing healthier beverage choices during childhood can promote better oral health outcomes and significantly reduce future dental problems.
Parental Awareness and Education
Recent research has underscored the significant impact that soda consumption can have on children’s dental health. Parents and guardians play a crucial role in shaping their children’s dietary habits, making parental awareness essential in mitigating the adverse effects of sugary beverages. Educating parents about the ramifications of soda on dental health can empower them to make informed choices that promote healthier habits for their children.
One effective strategy is to provide parents with accessible information about the relationship between soda consumption and dental issues such as cavities and enamel erosion. Numerous studies indicate that regular intake of sugary drinks can lead to an increase in acid production in the mouth, which harms tooth enamel over time. By highlighting these potential consequences, parents may become more inclined to limit their children’s soda intake and replace it with healthier alternatives like water or milk.
Moreover, schools and community organizations can play a pivotal role by organizing workshops or informational sessions aimed at educating parents on healthy beverage choices. These programs can include demonstrations on how to read nutritional labels, understanding sugar content, and the importance of maintaining regular dental check-ups. Encouraging dialogues about dental hygiene and nutrition at home further reinforces the significance of avoiding sugary drinks.
Additionally, fostering positive habits at an early age is vital. Parents can model appropriate behavior by choosing healthier options themselves, thereby setting a precedent for their children. Introducing naturally flavored water or homemade fruit juices as alternatives to soda can also make healthier choices more appealing to younger audiences. Ultimately, enhancing parental awareness and education around the negative effects of soda on dental health is an indispensable step in cultivating lifelong health-conscious behaviors in children.
Strategies to Reduce Soda Intake
Reducing soda intake among children can significantly benefit their dental health and overall well-being. Parents and caregivers can implement several practical strategies to encourage healthier beverage choices. One effective approach is to provide appealing alternatives to soda. For instance, flavored water or homemade fruit-infused beverages can be enticing substitutes. By combining water with slices of citrus fruits, berries, or even herbs like mint, caregivers can create refreshing drinks that mimic some of the flavors children enjoy in sodas, but without the high sugar content.
Additionally, promoting healthy snacking can help divert children’s attention from soda consumption. Offering nutrient-rich snacks, such as cut vegetables with hummus, yogurt with fresh fruits, or whole-grain crackers, can keep children satisfied while reducing the likelihood of reaching for sugary drinks. Educating children about the benefits of these healthier options can foster an appreciation for nutritious foods and drinks.
Hydration is key in minimizing soda cravings. Parents should emphasize the importance of drinking enough water throughout the day. Encouraging kids to carry a reusable water bottle not only promotes hydration but also establishes a habit of choosing water over sugary beverages. In settings where soda is more readily available, such as parties or playdates, parents can provide healthier beverage options, thereby taking a proactive approach in health-conscious decision-making.
Lastly, modeling balanced dietary behaviors is essential. When children witness their parents and caregivers opting for water or nutritious drinks over soda, they are more likely to emulate these choices. It is vital for families to engage in discussions about healthy eating habits, making it a collective effort to promote a balanced diet. By adopting these strategies, families can collectively work toward reducing soda intake among children, thereby supporting better dental and overall health in the long term.
Recommendations From Dental Experts
Maintaining good dental health in children is of paramount importance, and various recommendations from dental experts can significantly contribute to this goal. One of the primary suggestions is to ensure regular dental check-ups. These visits allow for monitoring of children’s oral health, early detection of potential issues, and professional cleanings that remove plaque buildup. Most dental experts recommend that children should visit a dentist every six months to establish a routine of preventive care.
Another critical aspect is the adoption of proper brushing techniques. Dental professionals emphasize the importance of teaching children how to effectively brush their teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and ensuring that children learn to brush for at least two minutes is essential for effective plaque removal. Additionally, parents should supervise young children to ensure they develop the habit of brushing correctly from an early age.
Dietary choices also play a vital role in supporting children’s dental health. Dental experts advise parents to promote a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products while limiting sugary snacks and beverages, especially soda. Sugary foods and drinks are known to increase the risk of cavities, as they provide fuel for harmful bacteria in the mouth. Furthermore, it is crucial to encourage children to drink water, particularly fluoridated water, which can help strengthen tooth enamel and promote overall oral health.
Implementing these recommendations, including regular dental visits, proper brushing techniques, and healthy dietary practices, can significantly reduce the risk of dental problems and help ensure that children’s teeth remain healthy and strong as they grow. Engaging children in their oral health journey fosters lifelong good habits that contribute to optimal dental health.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In reviewing the impact of soda on children’s dental health, it has become increasingly clear that the adverse effects of sugar-filled beverages cannot be overlooked. Research indicates that soda consumption is linked to a higher incidence of cavities, enamel erosion, and other dental problems in children. The acidic nature and high sugar content of sodas exacerbate the likelihood of dental issues, necessitating a proactive approach to dietary habits among young individuals.
It is vital for parents, educators, and healthcare providers to recognize the importance of monitoring soda intake and implementing better nutritional choices for children. Replacing soda with healthier alternatives, such as water or milk, can significantly contribute to improved dental health. Furthermore, cultivating an understanding among children regarding the consequences of excessive sugar consumption is essential for fostering lifelong healthy habits. Parents should also emphasize the significance of regular dental check-ups, which can help identify and mitigate potential dental issues at an early stage.
To facilitate these changes, it is essential to create supportive environments. Schools, for example, can play a pivotal role by offering healthy beverage options and conducting educational programs about nutrition and oral hygiene. Encouraging community initiatives focused on reducing soda consumption can also foster a culture of health. As engaged members of society, readers are encouraged to share the insights gained from this research with friends, family, and community members. By raising awareness about the impact of soda on children’s dental health, we can collectively work towards promoting healthier habits and ensuring better dental outcomes for future generations.